Customized Systems
Microtomography, SRS, Coherent Raman, Stimulated Raman
Microtomography and SRS of Microfossils for Paleoclimate Reconstruction
The structure and morphology of microfossils are mainly studied by optical microscopes, electron microscopes and micro-Computed tomography μ-CT. However, getting accurate three dimensional structures of microfossils with these techniques can be challenging in terms of measurement accuracy and analysis duration. Tomographic stimulated Raman scattering microscopy enables to record 3D images of fossils in reasonable times, based on the minerals contained in a sample.
Installation Site: KU Leuven, Centre for Surface Chemistry and Catalysis, Netherlands
Inspired by: Maarten Roeffaers and Christian Steuwe, KU Leuven
Characterization of a Noble-Gas Filled Hollow-core Fiber Amplifier
SPIDER, Hollow-core Fiber Amplifier, Few-cycle
Pulse compression in a hollow-core fiber is an approach for the generation of very short fs-pulse durations. It is implemented in various ways, for instance, by spectral broadening in noble gas filled hollow-core fibers where the noble gas acts as a nonlinear medium. In this setup, SPIDER traces of such a system with extremely short pulses (few-cycles) and high pulse energies has been recorded. To cover the broad spectrum, an extended IR wavelength version (700 – 1300 nm) of a Few Cycle SPIDER has been realized by coupling an additional waveScan spectrometer.
Inspired by: Active Fiber Systems GmbH, Jena, Germany
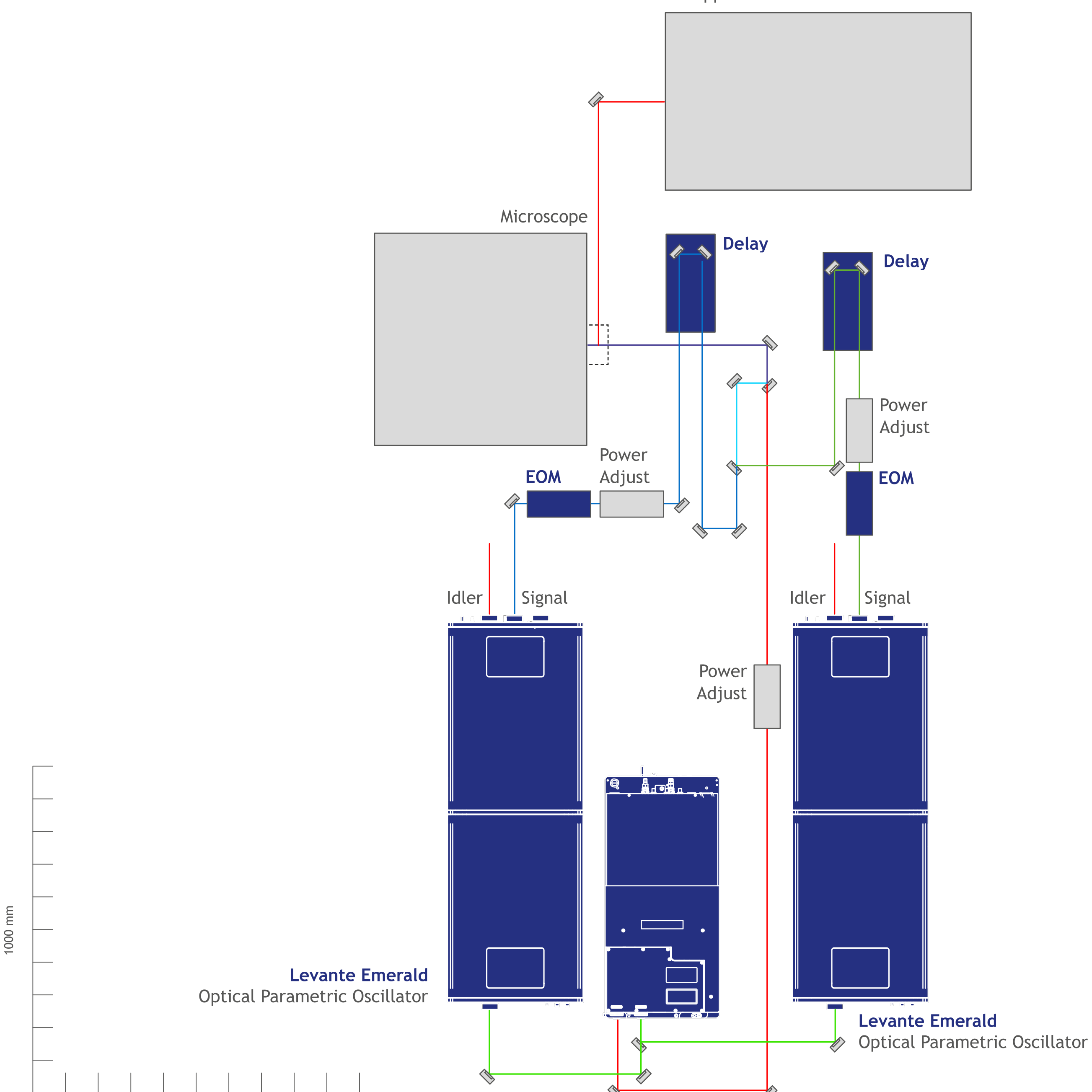
Two-Photon Resonance, Quantum Dots, Qubits, Semiconductor
Quantum-Dots: On-demand Generation of Entangled Photons Pairs
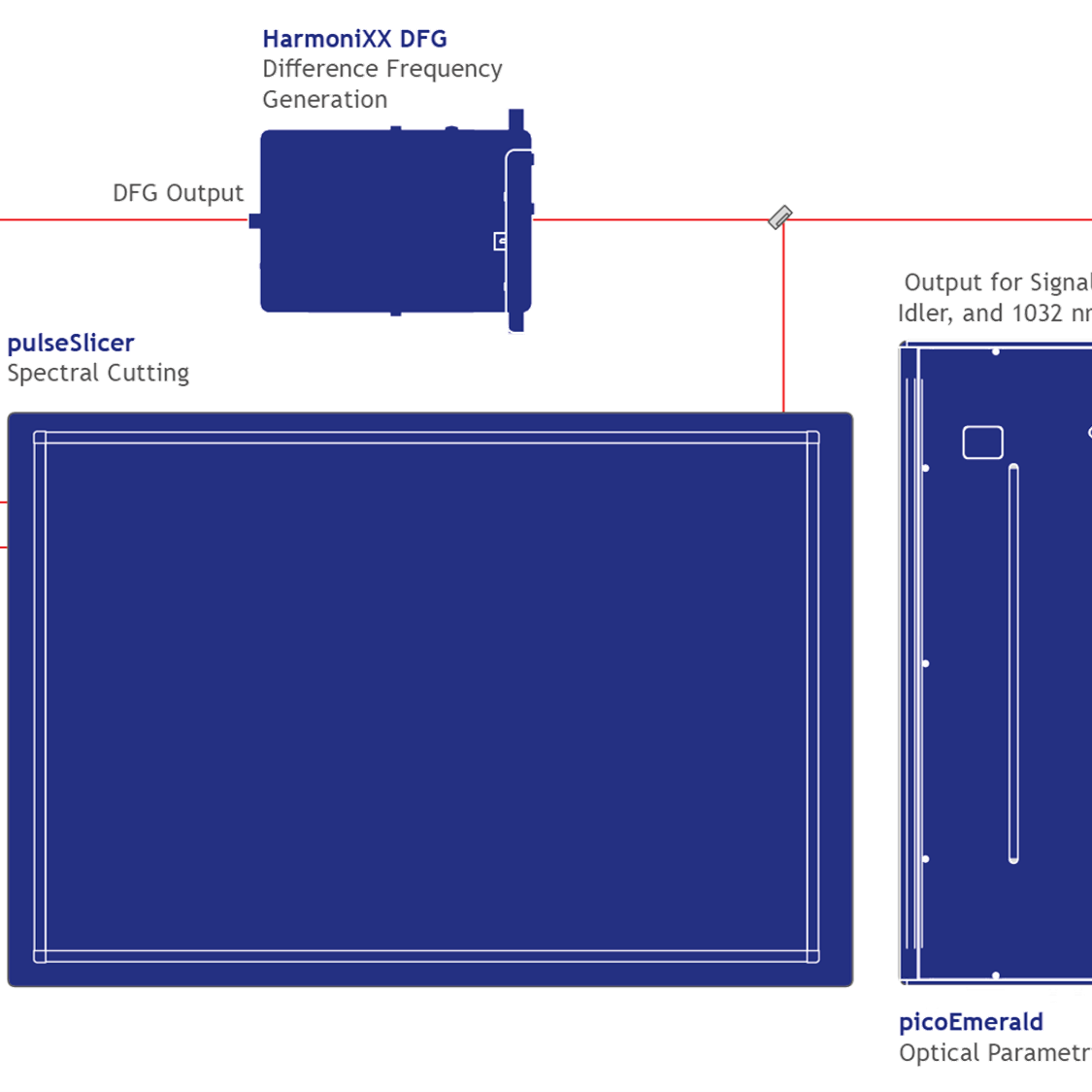
One of the very first requirements to generate ideal on-demand single photon emission from quantum dots (QD) is two-photon resonant excitation. The setup is used to create stable pico-second pulsed laser emission (picoEmerald) in a tunable range of about 700 – 1950 nm.
The wavelength range is further enhanced into the infrared region (DFG). To achieve best excitation parameters without interference of the QD excitation, a double pulseSlicer (for IR and for NIR) is incorporated for narrowing the broadband laser pulses by spectral cutting. The complete system is automated and allows wavelength setting via APE software.
Installation Site: The Quantum Nano Photonics (QNP) group is part of the Department of Applied Physics at the School of Engineering Sciences located in Stockholm, Sweden.
Inspired by: Klaus Joens, KTH Stockholm, Sweden
Angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy, UV, Photoelectron Spectroscopy
Laser ARPES With a High Power Tunable ps UV Source
Laser-based ARPES (Angle-Resolved Photo-Emission Spectroscopy) is a form of ARPES that uses a laser as the light source. Comparing to a synchrotron light source, laser-based ARPES offer some advantages: It fits on a table (ok … a large table) and makes experiment schedules independent from rare beam times at synchrotron facilities. The UV-laser provides an ultra-high energy resolution of down to 0.1 meV while providing a very high photon flux.
Installation Site: SPECS Nano Surface Analysis GmbH, Germany
Inspired by: Thorsten Kampen, SPECS